What are postbiotics?

Postbiotics are one of the hottest topics and the newest member of the ‘biotic’ family! You have heard of prebiotics which are the food for bacteria and probiotics which are beneficial live bacteria. Now we have postbiotics which are the substances that live bacteria produce. The news around postbiotics is how these end products of bacterial metabolism can have therapeutic benefits.
Bacteria with benefits – PRE, PRO, and POST biotics
Like all living things, bacteria need the right environment to survive and produce something. You may be wondering how prebiotics, probiotics and now postbiotics are related to each other. And how are postbiotics connected to the trending business of fermented foods and supplements?
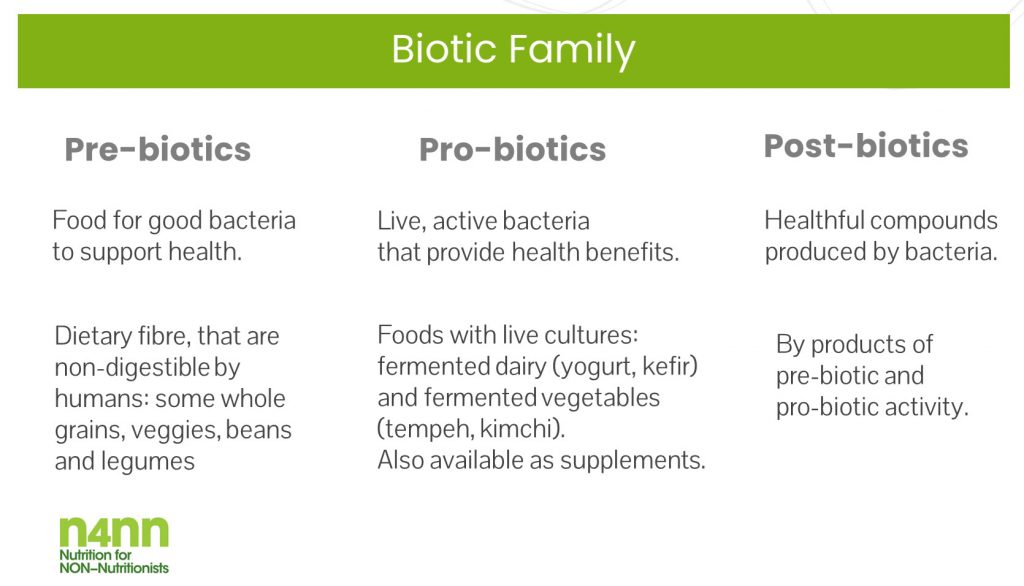
- Pre-biotics are FOOD for the bacteria. In the food we eat, prebiotic compounds are not digested but provide fuel for gut bacteria to grow to support health. Some foods naturally high in prebiotics are also a source of fibre such as whole grains, fruit, vegetables, beans and legumes. Examples include Jerusalem artichokes, chicory, garlic, onion, asparagus, cabbage, chickpeas, lentils, red kidney beans and soybeans.
- Pro-biotics are LIVE organisms that have scientifically proven health benefits if consumed in adequate amounts. Foods that contain probiotics (live friendly bacteria) include fermented dairy (yogurt, kefir) and fermented vegetables (uncooked sauerkraut, traditional kimchi). Probiotics are also available as dietary supplements.
- Post-biotics are compounds that bacteria produce as part of their life cycle and metabolism. For example, bacteria and yeast strains used in fermentation generate postbiotic compounds. These include short-chain fatty acids, functional proteins along with discarded matter from the microorganisms themselves, which include cell wall components. Postbiotics also include nutrients such as vitamins B and K, amino acids and substances called antimicrobial peptides that help to slow down the growth of harmful bacteria.
Postbiotics are studied closely for potential health benefits. They may help reduce digestive symptoms, optimize gut flora and advance the immune response of the colon’s lining by improving gut barrier function. Researchers are also looking at anti-inflammatory, antiobesogenic, antihypertensive, hypocholesterolemic, antiproliferative and antioxidant activities.
Although scientists and gut experts have known about postbiotics and their benefits for years, no regulators have provided a definition for postbiotics or a framework specific to postbiotic-containing foods or food supplements. However, a proposed definition was recently published by a team of experts who defined postbiotics as a “preparation of inanimate microorganisms and/or their components that confers a health benefit on the host.” The expert panel determined that a definition of postbiotics is useful so that scientists, industry, regulators and consumers have common ground for future activity in this area. It’s hoped that a generally accepted definition will lead to regulatory clarity and promote innovation and the development of new postbiotic products (Salmien et al.).
What can you say about biotics?
Terms such a prebiotic and probiotic may suggest a food provides a specific health benefit and are therefore considered health claims. Health claims are subject to the Canadian Food and Drugs regulations and must not be false, misleading or deceptive. These implied health claims are only acceptable when accompanied by a statement of the specific and measurable health benefit conferred by the prebiotic substance, as demonstrated in humans (Health Canada).
Postbiotics are likely to be the next health-boosting compound for digestive health and more. They have the advantage of longer shelf life in comparison to live, active probiotics. However postbiotics are not yet regulated in many countries. Consult a food labelling expert for guidance.
Bottom line:
The biotic family supports a healthy gut. For optimal health, scientists recommend a combination approach—prebiotic fiber to feed gut bacteria as well as live probiotics to provide specific health benefits and create postbiotic compounds.
Connect with us (Info@n4nn.ca) and let’s work together for your innovation journey. As dietitians, we can support you and your business in taking meaningful steps toward health and wellness.
References:
- Salminen, S.,et al. (2021). The International Scientific Association of Probiotics and Prebiotics (ISAPP) consensus statement on the definition and scope of postbiotics. Nature reviews. Gastroenterology & hepatology, 18(9), 649–667. Accessed Dec 9, 2021 from https://doi.org/10.1038/s41575-021-00440-6
- Golen, T., Riccotti H. (2021). What are postbiotics? Harvard Health Publishing. Accessed Dec 9, 2021 from https://www.health.harvard.edu/nutrition/what-are-postbiotics
- Hermann, M. (2020). Discover the World of Postbiotics, Today’s Dietitian Vol. 22 (6):20.
- Health Canada (2019). Health claims on food labels / Prebiotic claims, Probiotic claims. Accessed Dec 9, 2021 from Health claims on food labels – Food label requirements – Canadian Food Inspection Agency (canada.ca)